Ang email dili mahimong walay sulod
Ang password dili mahimong walay sulod
Sayop sa format sa email
Ang email dili mahimong walay sulod
Anaa na ang email
6-20 ka karakter (mga letra ug numero lamang)
Ang password dili managsama
Sayop sa format sa email
Ang email dili mahimong walay sulod
Wala ang email
6-20 ka karakter (mga letra ug numero lamang)
Ang password dili managsama

Balita
Common Casting Defects of Ductile Iron and Their Solutions
Ductile iron is generally obtained by spheroidization and inoculation to obtain a spherical graphite, which effectively improves the mechanical properties, plasticity and toughness of cast iron, thereby obtaining a higher strength than carbon steel. Ductile iron is a high-strength cast iron material developed in the 1950s. Its comprehensive performance is close to that of steel. Based on its excellent performance, it has been successfully used in some castings with relatively complex forces, strength, toughness, and resistance. Among the parts with high grinding requirements. Ductile iron has rapidly developed into a widely used cast iron material, second only to gray cast iron. The so-called "replacing steel with iron" mainly refers to ductile iron.
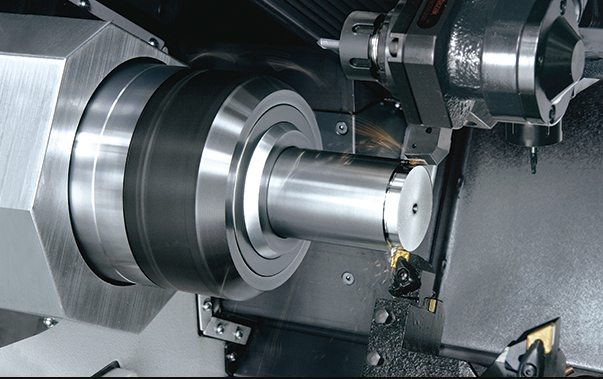
In the casting process, ductile iron improves its mechanical properties, plasticity and tensile strength through spheroidization and inoculation treatment. Based on this physical property, the use of carbon steel has been replaced in many use cases. In order to cast qualified ductile iron castings, it is necessary to strictly control the production quality of ductile iron and avoid casting defects to affect its physical properties. The problems that are more likely to occur in the casting process are as follows.
Common defects of ductile iron
✅Subcutaneous stoma:
Subcutaneous pores are difficult to find on the surface after casting. They often appear in the processing process, especially large ductile iron castings are very prone to this problem. The formation of pores is mainly related to hydrogen and carbon monoxide. When casting, the temperature of molten iron in the cavity fills the cavity with the runner. If the casting time is too long, the temperature difference of molten iron will increase, resulting in that hydrogen and carbon monoxide cannot be discharged in time, and they will be sealed under the skin that solidifies first. Circular or oval pores of varying sizes are formed.
Solution:
- Increase the temperature of molten iron during casting.
- Reasonably set the position and size of the runner during modeling, and increase the exhaust riser appropriately to make the molten iron flow smoothly so that the cavity can be quickly filled.
✅Graphite float:
After the casting is completed, a large amount of graphite material is found on the surface of the casting when the surface sand is removed. This phenomenon is caused by graphite floating. The reason for this is that the cooling rate of the molten iron cannot meet the relevant requirements, which leads to the precipitation of large-diameter graphite and accumulation on the upper part of the casting, thus affecting the physical performance of the casting.
Solution: Adjust the content of carbon and silicon in ductile iron to reduce the occurrence of graphite floating. Furthermore, adjusting the cooling time and speed of the molten iron can also prevent the graphite from floating.
✅Shrinkage shrinkage:
During casting, the molten metal fills the cavity quickly, and the eutectic expansion force increases accordingly. If the strength of the mold cannot meet the requirements, the overall shape of the casting will increase (the phenomenon of box expansion), which will cause the liquid metal in the normal riser. It cannot be properly fed, resulting in the problem of shrinkage porosity. Usually the problem will be concentrated in the part where the wall thickness is too large.
Solution: Improve the strength of the casting mold, reasonably increase the weight of the press box iron, and reasonably set the size and position of the feeding riser.
Last few words
For more information about cast iron skillets for sale,cast iron cooker,cast iron products, we are glad to answer for you.

